Explain the triple constraint and its importance in project management.
The triple constraint involves project changes such as
-Cost: How much money is involved.
-Scheduale: How much time the activity will take.
-Scope: The type of quality the end result should achieve.
The importance of this in project management is that it helps businesses to allocate how resources will be used within the project.
http://brianherman.wordpress.com/2008/10/20/risky-business/
Describe the two primary diagrams most frequently used in project planning
Two primary diagrams that are frequently used include
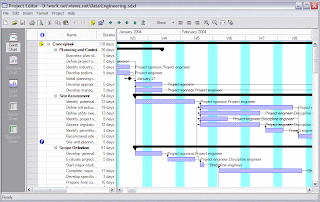
- Gantt chart which shows when each task is due to completed. On the vertical axis, the names of tasks are displayed and on the horizontal axiz is where the time is presented.
- PERT chart which shows the tasks and relationships of a project. The PERT chart comprises of two things: a dependency and a critical path.
Below: Example of a commonly used Gantt chart
http://www.gantt-chart.biz/gantt-charting-made-easy/
Below: An example of a commonly used Pert Chart
http://www.spottydog.u-net.com/guides/faq/faq.html
Identify the three primary areas a project manager must focus on managing to ensure success
To ensure success, a project manager much focus on:
• Managing People
• Managing Communications
• Managing Change
Outline 2 reasons why projects fail and two reasons why projects suceed.
Below is a chart which outlines why projects fail and succeed.
Mary Ann's Blog
Tuesday, October 19, 2010
Week Ten - Customer Relationship Management and BI
What is your understanding of CRM?
CRM stands for Customer Relationship Management. It is an information industry term that helps manage customer relationships in an organised way. For example, a company might build a database about its customers decribed with enough information so all sectors in the company could access the information needed to create products, send out new offerings and creating new forms of advertisements.
CRM enables:
- Industries to find their best/ loyal customers and create a database based on their needs and wants.
- Industries to create a more personalised approach to each of their customers.
Below: Video explaining CRM
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=s6XN0j9F3Yo
Compare operational and analytical customer relationship management.
Analytical-- Is a DSS (Decision Support System) targeted to help senior executives, marketers and sales divisions to better understand their customers, in ways such as:
* Getting to know the company's interaction with their customers.
* Finding out customer's buying cycle (e.g- what times in the yr do they mostly purchase a certain item)
Operational-
- Directly provides help and support for front line services in all sectors of a company. This includes:
* Sales, customer service and marketing divisions.
- It highly relies on computer technology to achieve its goals.
Describe and differentiate CRM technologies used by marketing departments and sales departments:
Marketing Departments:
List generator – compiles customer information from a variety of sources and segment the information for different marketing campaigns.
Campaign management system – guides users through marketing campaigns.
Cross-selling – selling additional products or services.
Up-selling – increasing the value of the sale.
Sales Departments
Sales management CRM system – automates each phase of the sales process, helping individual sales representatives coordinate and organize all of their accounts.
Contact management CRM system – maintains customer contact information and identifies prospective customers for future sales.
Opportunity management CRM system – targets sales opportunities by finding new customers or companies for future sales.
How could a sales department use operational CRM technologies?
By the use of the following operational CRM technologies, sales departments could discover:
Sales management CRM system- Number of sales calls
Contact management CRM system- Number of current and new customers
Opportunity management CRM system- New and exsisting revenue
These systems make it easier to keep track of trends and changes occuring in the sales departments within the operations front line. By looking at changes over the years, this would help to see where their strengths and weaknesses lie for future changes.
Describe business intelligence and its value to businesses
Business intelligence (BI) are technologies and applications used to collect, organise and analyse data and information to support decision making efforts. An example of this includes data mining. It has very high value in a business as it is relied on for many different aspects such as Pivot Table on Microsoft Access. BI enables companies to make decisions based on current and future trends and helps to organise and plan them in a sequential order while putting into account the time needed to complete each task.
Below: An example of BI
Explain the problem associated with business intelligence. Describe the solution to this business problem
As companies may have alot of data, they may not benefit from turning it into meaningful information and useful data for analytical and strategic decision making. This could be the result of not having the right software to generate sucessful outputs. The problem with today's organisations is that some find it hard to understand all their strengths and weaknesses. The result could be from all departments not having access to the data for them to interpret it into useful information. The problem that many face in the end is data rich and infomation poor.
Below: A video expample of problems occuring with business intelligence
The two possible outcomes a company could get from data miming are:
CRM stands for Customer Relationship Management. It is an information industry term that helps manage customer relationships in an organised way. For example, a company might build a database about its customers decribed with enough information so all sectors in the company could access the information needed to create products, send out new offerings and creating new forms of advertisements.
CRM enables:
- Industries to find their best/ loyal customers and create a database based on their needs and wants.
- Industries to create a more personalised approach to each of their customers.
Below: Video explaining CRM
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=s6XN0j9F3Yo
Compare operational and analytical customer relationship management.
Analytical-- Is a DSS (Decision Support System) targeted to help senior executives, marketers and sales divisions to better understand their customers, in ways such as:
* Getting to know the company's interaction with their customers.
* Finding out customer's buying cycle (e.g- what times in the yr do they mostly purchase a certain item)
Operational-
- Directly provides help and support for front line services in all sectors of a company. This includes:
* Sales, customer service and marketing divisions.
- It highly relies on computer technology to achieve its goals.
Describe and differentiate CRM technologies used by marketing departments and sales departments:
Marketing Departments:
List generator – compiles customer information from a variety of sources and segment the information for different marketing campaigns.
Campaign management system – guides users through marketing campaigns.
Cross-selling – selling additional products or services.
Up-selling – increasing the value of the sale.
Sales Departments
Sales management CRM system – automates each phase of the sales process, helping individual sales representatives coordinate and organize all of their accounts.
Contact management CRM system – maintains customer contact information and identifies prospective customers for future sales.
Opportunity management CRM system – targets sales opportunities by finding new customers or companies for future sales.
How could a sales department use operational CRM technologies?
By the use of the following operational CRM technologies, sales departments could discover:
Sales management CRM system- Number of sales calls
Contact management CRM system- Number of current and new customers
Opportunity management CRM system- New and exsisting revenue
These systems make it easier to keep track of trends and changes occuring in the sales departments within the operations front line. By looking at changes over the years, this would help to see where their strengths and weaknesses lie for future changes.
Describe business intelligence and its value to businesses
Business intelligence (BI) are technologies and applications used to collect, organise and analyse data and information to support decision making efforts. An example of this includes data mining. It has very high value in a business as it is relied on for many different aspects such as Pivot Table on Microsoft Access. BI enables companies to make decisions based on current and future trends and helps to organise and plan them in a sequential order while putting into account the time needed to complete each task.
Below: An example of BI
Explain the problem associated with business intelligence. Describe the solution to this business problem
As companies may have alot of data, they may not benefit from turning it into meaningful information and useful data for analytical and strategic decision making. This could be the result of not having the right software to generate sucessful outputs. The problem with today's organisations is that some find it hard to understand all their strengths and weaknesses. The result could be from all departments not having access to the data for them to interpret it into useful information. The problem that many face in the end is data rich and infomation poor.
Below: A video expample of problems occuring with business intelligence
What are two possible outcomes a company could get from using data mining?
The two possible outcomes a company could get from data miming are:
- Increase profits and allow an organisation to have better sales and confined resources.
- Statistical analysis: Consists of assessing the data trends throught the help of a regression analysis and statistics. This allows emmployees to construct statistical models and to compare which is more suitable to be used in the organisation.
Monday, September 20, 2010
Week Nine - Operations Management and Supply Chain
1. Define the term operations management
Operations manaegement in a firm is based accross all departments and consists of converting resources from inputs to outputs. For example, an online travel agent creating holiday packages for customers. The input is all the airfares, hotels, and tours. The output is the itinerary with the final price for the package.
2. Explain operations management’s role in business
Operation managers control the flow of inputs and outputs in an organisation. Their role consists of:
Forecasting: knowing when particular services need to be done during the year.
Capacity planning: how much inputs are needed to make outputs.
Schedualling: need to have a system in place stating who does what and by when
Managing inventory: the more inventory held, more money is spent which could go towards other things.
Assuring quality: ensuring the quality of the input matches the output product
Training and motivating employees: ensuring all employees are properly trained and are motivated will create better output by them.
Locating facilities: delegating the right inputs to the right departments will increase better chances of output.
3. Describe the correlation between operations management (OM) and information technology (IT)
Modern OM relies heavily on IT that OM can not do their jobs without IT. OM allows managers to:
- Find out what resources and how much of it is needed.
- Know when the work needs to be done
- Know where the work will be carried out
- Know how the work will be performed
- Who will take part in doing the work
4. Explain supply chain management and its role in a business
Supply chain management consists of managing the flow of information between and among stages in a supply chain to increase the profitability and effectiveness in the total supply chain. Its role is important in a business as it allows more efficiency in its productions of good and services- being more effecting and efficent in turning inputs into outputs.
5. List and describe the five components of a typical supply chain
•Supplier: supplies the raw materials (also known as inputs) to the manufacturer.
•Manufacturer: produces raw materials into products (also known as outputs) for distribution.
•Distributor: recieves the products form the manufacturer in bulk and sells to retailers.
•Retailer: sells the products to customers (known as target market).
•Customer: known as the end party consume the product purchased.
Dis-intermediation is caused from the use of eCommerce. This is known as the removal of stages in the supply chain (e.g: customer directly dealing with the manufacturer, instead of through the retailer).
Below: an example of travel and tourism supply chain
6. Define the relationship between information technology and the supply chain.
In the supply chain, IT plays an important role. It is relied on to make accurate decisions reflecting each step in the supply chain. Without IT, businesses would be either
- Creating too much stock which is not selling
- Creating too little stock which is in high demand
With the help of IT, businesses are able to keep record on how much stock is available at present, how much needs to be orded in the future and also make decisions to whether profits are being generated from the goods sold and whether they should contine to produce them or not.
Below: video shows examples of ways to control stock
Operations manaegement in a firm is based accross all departments and consists of converting resources from inputs to outputs. For example, an online travel agent creating holiday packages for customers. The input is all the airfares, hotels, and tours. The output is the itinerary with the final price for the package.
2. Explain operations management’s role in business
Operation managers control the flow of inputs and outputs in an organisation. Their role consists of:
Forecasting: knowing when particular services need to be done during the year.
Capacity planning: how much inputs are needed to make outputs.
Schedualling: need to have a system in place stating who does what and by when
Managing inventory: the more inventory held, more money is spent which could go towards other things.
Assuring quality: ensuring the quality of the input matches the output product
Training and motivating employees: ensuring all employees are properly trained and are motivated will create better output by them.
Locating facilities: delegating the right inputs to the right departments will increase better chances of output.
3. Describe the correlation between operations management (OM) and information technology (IT)
Modern OM relies heavily on IT that OM can not do their jobs without IT. OM allows managers to:
- Find out what resources and how much of it is needed.
- Know when the work needs to be done
- Know where the work will be carried out
- Know how the work will be performed
- Who will take part in doing the work
4. Explain supply chain management and its role in a business
Supply chain management consists of managing the flow of information between and among stages in a supply chain to increase the profitability and effectiveness in the total supply chain. Its role is important in a business as it allows more efficiency in its productions of good and services- being more effecting and efficent in turning inputs into outputs.
5. List and describe the five components of a typical supply chain
•Supplier: supplies the raw materials (also known as inputs) to the manufacturer.
•Manufacturer: produces raw materials into products (also known as outputs) for distribution.
•Distributor: recieves the products form the manufacturer in bulk and sells to retailers.
•Retailer: sells the products to customers (known as target market).
•Customer: known as the end party consume the product purchased.
Dis-intermediation is caused from the use of eCommerce. This is known as the removal of stages in the supply chain (e.g: customer directly dealing with the manufacturer, instead of through the retailer).
Below: an example of travel and tourism supply chain
6. Define the relationship between information technology and the supply chain.
In the supply chain, IT plays an important role. It is relied on to make accurate decisions reflecting each step in the supply chain. Without IT, businesses would be either
- Creating too much stock which is not selling
- Creating too little stock which is in high demand
With the help of IT, businesses are able to keep record on how much stock is available at present, how much needs to be orded in the future and also make decisions to whether profits are being generated from the goods sold and whether they should contine to produce them or not.
Below: video shows examples of ways to control stock
Tuesday, September 14, 2010
Week 8 - Networks and Wireless
1.Explain the business benefits of using wireless technology.
• Connect to the network any time: by the use of LANs and WANs, employees could process their work outside of the office.
• Can process, send and receive information at any location: broadband allows access to the internet anywhere in the office building.
• Less cable lines used means more space in the office: therefore there would be more space to move around and less wires on the floor reduces hazards in the office.
2.Describe the business benefits associated with VoIP
VOIP enables phone calls, faxes, voice mail, e-mail and Web conferences over digital networks.
It saves money by:
3. Compare LANs and WANs
LAN- Local Area Network
• Connects a group of computers together that are located in the same geographical area.
• The computers could be located at home, within a company or school network.
• Most are built using Ethernet cables, networks and hubs.
• The smallest LAN consists of 2 computers and a large LAN can consist of thousands of computers.
Below: Image of a LAN structure in a workplace
WAN- Wide Area Network
• Connect computers together located in regional or national boundaries.
• WANs are usually built for organisations and are usually private.
• Usually built using a lease line which is quite expensive.
Below: The image shows a typical set up of a WAN within an office environment
http://www.virtualpro.co.uk/2009/08/08/citrix-branch-repeater-wan-acceleration-branch-office-in-a-box/
4.Describe RFID and how it can be used to help make a supply chain more effective.
RFID- Radio Frequency Identification provides a unique identification for certain devices. They are small electronic devices which once are scanned can retrieve data which is stored on it
They can help a supply chain by easily identifying what is in the shopper’s grocery bag and adding up the total price. RFID are more effective and efficient from barcodes as they use up less time from individually scanning each item.
Below: example of how RFID is used on wine bottles instead of barcodes
5. Identify the advantages and disadvantage of deploying mobile technology
Advantages
• Accessed anytime and anywhere
• Can send and receive both text, pictures and videos on the go
• Easier to access information whenever it is needed
• Don’t need to connect your phone to a wireless network as you mobile phone provider can provide the connection.
Disadvantages
• Mobile phone screens can be quite small to see the text at times
• Some devices are not able to open certain pages due to the software it uses
• People become dependent on their mobile
• Unable to print from your mobile
• Connect to the network any time: by the use of LANs and WANs, employees could process their work outside of the office.
• Can process, send and receive information at any location: broadband allows access to the internet anywhere in the office building.
• Less cable lines used means more space in the office: therefore there would be more space to move around and less wires on the floor reduces hazards in the office.
2.Describe the business benefits associated with VoIP
VOIP enables phone calls, faxes, voice mail, e-mail and Web conferences over digital networks.
It saves money by:
- Running over an existing network
- Calling over the internet with no bill attached.
3. Compare LANs and WANs
LAN- Local Area Network
• Connects a group of computers together that are located in the same geographical area.
• The computers could be located at home, within a company or school network.
• Most are built using Ethernet cables, networks and hubs.
• The smallest LAN consists of 2 computers and a large LAN can consist of thousands of computers.
Below: Image of a LAN structure in a workplace
WAN- Wide Area Network
• Connect computers together located in regional or national boundaries.
• WANs are usually built for organisations and are usually private.
• Usually built using a lease line which is quite expensive.
Below: The image shows a typical set up of a WAN within an office environment
http://www.virtualpro.co.uk/2009/08/08/citrix-branch-repeater-wan-acceleration-branch-office-in-a-box/
4.Describe RFID and how it can be used to help make a supply chain more effective.
RFID- Radio Frequency Identification provides a unique identification for certain devices. They are small electronic devices which once are scanned can retrieve data which is stored on it
They can help a supply chain by easily identifying what is in the shopper’s grocery bag and adding up the total price. RFID are more effective and efficient from barcodes as they use up less time from individually scanning each item.
Below: example of how RFID is used on wine bottles instead of barcodes
5. Identify the advantages and disadvantage of deploying mobile technology
Advantages
• Accessed anytime and anywhere
• Can send and receive both text, pictures and videos on the go
• Easier to access information whenever it is needed
• Don’t need to connect your phone to a wireless network as you mobile phone provider can provide the connection.
Disadvantages
• Mobile phone screens can be quite small to see the text at times
• Some devices are not able to open certain pages due to the software it uses
• People become dependent on their mobile
• Unable to print from your mobile
Monday, September 6, 2010
Week 7- Database and Data Warehouse
1. List, describe, and provide an example of each of the five characteristics of high quality information.
Accuracy: Information needs to be accurate and high quality. High accuracy will allow organisations to meet their goals. E.g: Excel spreadsheets designed to report monthly sales figures for a clothes store.
Completeness: Gives a big part of the picture of the information being reported. E.g: Total sales figures of a shoe store for the whole year.
Consistency: It is important to keep information reported consistant, to keep all added information on the same level as what was previously reported. E.g: When adding a telephone no. in the field, the field wont accept more than a 10 digit number to reduce inaccuracy.
Uniqueness: In order to add value to an organisation, information must be unique and distinctive. E.g:Is the information available on other sites?
Timeliness: New and current data is more valuable to an organisation than old and outdated information. It is important to keep up to date with information, as the era is more competitive. Eg: Real time information.
2. Define the relationship between a database and a database management system.
Database: A collection of organised information that allows data to be manipulated or extracted to suit the reporting needs.
Database management system: A set of programs used for managing the database. It facilitates the creation and maintenance and use of an electronic database.
3. Describe the advantages an organisation can gain by using a database.
Increased flexibility:
- Handles changes quickly and easily.
- Provides users with different views.
Increased scalability and performance
-scalability: How well a system can adapt to increased demands.
-Performance: measures how quicky a system performs a certain process or transaction.
Increased information integrity (quality)
Assurance that the information has not been changed or altered since the last time accessed.
Increased information security
- Information must be protected as it is an organisational asset. This is controlled through passwords and access controls.
An example of a database is MySQL is below
4. Define the fundamental concepts of the relational database model.
A database system in which any database file can be part of more than one of the database's tables.
5. Describe the benefits of a data-driven website.
Development- Allows owner to make changes to website at anytime-> user friendly.
Content Management- A static website required a programmer to make updates. This can lead to misunderstandings to desired changes.
Future Expandability- Allows the site to grow faster allowing changes to be easily updated.
6. Describe the roles and purposes of data warehouses and data marts in an organisation
Roles-
Data Warehouses
A logical gathering of information from different databases supporting business analysis and decision making.
Data Marts
Contains a subset (a set of numbers who are part of another set) of data warehouse information.
Purposes-
Data Warehouses
To aggregate information through the organisation into a single location of storage, so employees can make decsions and undertake business activities. Therefore the information stored to support decision making processes.
Below is an image showing an example of data warehouse
Data Mart
Focuses on informational subsets depending on the needs of a business unit such as finance or production.
Below is an image showing the components that make up a data mart
Accuracy: Information needs to be accurate and high quality. High accuracy will allow organisations to meet their goals. E.g: Excel spreadsheets designed to report monthly sales figures for a clothes store.
Completeness: Gives a big part of the picture of the information being reported. E.g: Total sales figures of a shoe store for the whole year.
Consistency: It is important to keep information reported consistant, to keep all added information on the same level as what was previously reported. E.g: When adding a telephone no. in the field, the field wont accept more than a 10 digit number to reduce inaccuracy.
Uniqueness: In order to add value to an organisation, information must be unique and distinctive. E.g:Is the information available on other sites?
Timeliness: New and current data is more valuable to an organisation than old and outdated information. It is important to keep up to date with information, as the era is more competitive. Eg: Real time information.
2. Define the relationship between a database and a database management system.
Database: A collection of organised information that allows data to be manipulated or extracted to suit the reporting needs.
Database management system: A set of programs used for managing the database. It facilitates the creation and maintenance and use of an electronic database.
3. Describe the advantages an organisation can gain by using a database.
Increased flexibility:
- Handles changes quickly and easily.
- Provides users with different views.
Increased scalability and performance
-scalability: How well a system can adapt to increased demands.
-Performance: measures how quicky a system performs a certain process or transaction.
Increased information integrity (quality)
Assurance that the information has not been changed or altered since the last time accessed.
Increased information security
- Information must be protected as it is an organisational asset. This is controlled through passwords and access controls.
An example of a database is MySQL is below
4. Define the fundamental concepts of the relational database model.
A database system in which any database file can be part of more than one of the database's tables.
5. Describe the benefits of a data-driven website.
Development- Allows owner to make changes to website at anytime-> user friendly.
Content Management- A static website required a programmer to make updates. This can lead to misunderstandings to desired changes.
Future Expandability- Allows the site to grow faster allowing changes to be easily updated.
6. Describe the roles and purposes of data warehouses and data marts in an organisation
Roles-
Data Warehouses
A logical gathering of information from different databases supporting business analysis and decision making.
Data Marts
Contains a subset (a set of numbers who are part of another set) of data warehouse information.
Purposes-
Data Warehouses
To aggregate information through the organisation into a single location of storage, so employees can make decsions and undertake business activities. Therefore the information stored to support decision making processes.
Below is an image showing an example of data warehouse
Data Mart
Focuses on informational subsets depending on the needs of a business unit such as finance or production.
Below is an image showing the components that make up a data mart
Saturday, September 4, 2010
Week 6 - Chapter 5 Architectures
1. What is information architecture and what is information infrastructure and how do they differ and how do they relate to each other?
Information architecture: Consists of how to store files and where.
Information infrastructure: Consists of how the architecture works. How reliable and flexible it is, is important.
Differ-
Architecture: Is how the system will be used in the organisation. It includes all the systems and file paths involved in storing files.
Infrastructure: The way in which the files are stored and ensures that is runs well.
Relate-
Architecture relies on infrastructure as infrastructure ensures works behind the scenes to ensure that the files are stored properly and that the system is working well and is up to date with minimum error.
Below shows a link of how different infromation architecture looks like
http://www.prescientdigital.com/articles/strategic-design/design-ii-structure-comes-before-design
Below is an image showing how an information infrastucture on a national scale looks like
2. Describe how an organisation can implement solid information architecture
List and describe the five requirement characteristics of infrastructure architecture.
Implement solid information architecture-
By creating a blog site which enables employees and employers to create and distribute information within and amongst different sections of the organisation. This will be an easy and less time effective way to send messages and updates around the organisation.
Five requirement characteristics-
1. Flexibility – must meet all types of business changes. It is designed to include the ability to handle multiple currencies and languages, even if the company is not yet operating overseas.
2. Scalability – is how well a system can adjust to increased demands. Capacity planning determines the future IT infrastructure necessities for new equipment and additional network capacity.
3. Reliability – ensures all systems are functioning correctly and providing accurate information.
4. Availability – addresses when systems can be accessed by employees and customers. High availability refers to a system or component that is continuously operational for a desirably long length of time.
5. Performance – measures how quickly a system performs a certain process or transaction in terms of efficiency IT metrics of both speed and throughput.
3. Describe the business value in deploying service oriented architecture
A SOA will allow organisations to become integrated with other businesses which makes working together easier. It also ensures that IT systems can adapt quickly and rapidly to support business needs. Using Meta data, they can re use systems many times which makes development cheaper and flexible.
4. What is an event?
It is an event example which the flow of program is determined by events such as sensor outputs, the amounts of clicks per page or messages etc.
5. What is a service?
A service cab be a business task, such as checking a potential customer's credit rating. They are similar to software products.
6. What emerging technologies can companies use to increase performance and utilise their infrastructure more effectively?
-Virtualisation- enables division of recourses of a computer into different environments.
-Loose Coupling- services joined together on demand to create complex services.
-Grid computing- collection of dispersed computing, storage and network resources, used to improve quality of service.
Below is an example of a virtualisation desktop using Mac
Below is an image of how grid computing works
Information architecture: Consists of how to store files and where.
Information infrastructure: Consists of how the architecture works. How reliable and flexible it is, is important.
Differ-
Architecture: Is how the system will be used in the organisation. It includes all the systems and file paths involved in storing files.
Infrastructure: The way in which the files are stored and ensures that is runs well.
Relate-
Architecture relies on infrastructure as infrastructure ensures works behind the scenes to ensure that the files are stored properly and that the system is working well and is up to date with minimum error.
Below shows a link of how different infromation architecture looks like
http://www.prescientdigital.com/articles/strategic-design/design-ii-structure-comes-before-design
Below is an image showing how an information infrastucture on a national scale looks like
2. Describe how an organisation can implement solid information architecture
List and describe the five requirement characteristics of infrastructure architecture.
Implement solid information architecture-
By creating a blog site which enables employees and employers to create and distribute information within and amongst different sections of the organisation. This will be an easy and less time effective way to send messages and updates around the organisation.
Five requirement characteristics-
1. Flexibility – must meet all types of business changes. It is designed to include the ability to handle multiple currencies and languages, even if the company is not yet operating overseas.
2. Scalability – is how well a system can adjust to increased demands. Capacity planning determines the future IT infrastructure necessities for new equipment and additional network capacity.
3. Reliability – ensures all systems are functioning correctly and providing accurate information.
4. Availability – addresses when systems can be accessed by employees and customers. High availability refers to a system or component that is continuously operational for a desirably long length of time.
5. Performance – measures how quickly a system performs a certain process or transaction in terms of efficiency IT metrics of both speed and throughput.
3. Describe the business value in deploying service oriented architecture
A SOA will allow organisations to become integrated with other businesses which makes working together easier. It also ensures that IT systems can adapt quickly and rapidly to support business needs. Using Meta data, they can re use systems many times which makes development cheaper and flexible.
4. What is an event?
It is an event example which the flow of program is determined by events such as sensor outputs, the amounts of clicks per page or messages etc.
5. What is a service?
A service cab be a business task, such as checking a potential customer's credit rating. They are similar to software products.
6. What emerging technologies can companies use to increase performance and utilise their infrastructure more effectively?
-Virtualisation- enables division of recourses of a computer into different environments.
-Loose Coupling- services joined together on demand to create complex services.
-Grid computing- collection of dispersed computing, storage and network resources, used to improve quality of service.
Below is an example of a virtualisation desktop using Mac
Below is an image of how grid computing works
Wednesday, August 25, 2010
Week 5 - Ethics and Security
1. Explain the ethical issues surrounding information technology.
- Privacy Issues: Consists of the interest of the business for keeping valuable information away from the public. This relates to confidentiality. This is kept in mind when a company has valuable infromation which is wanted to be kept private. The risk of being released in the public could result to the company 'sinking'.
- Data Accuracy: It is important that data is keep up to date and is as accurate as possible. Constant checks must be made to ensure that no 'suspicious' activity has occured. Data must also be limited to who can access it to decrease amounts of malicious activity.
- Property Issues: Issues with who owns information in companies is a problem. It is shown that most companies are montioring employees' emails as they are misusing them with the information which is being issued out to peole outside of the company.
2. Describe a situation involving technology that is ethical but illegal
Employees search organisational database for sensitive and personal information. This is an example of bank employees who have access to customers' bank details and use it against their will to trace their bank details, which could lead to fraudulent activity such as taking money out of their accounts.
3. Describe and explain one of the computer use policies that a company might employee
Internet use policy- Consists of generalpriciples which guide the correct use of the internet in the workplace. The policy:
- Describes available internet services.
- Defines the purpose and restriction of internet access.
- Describes user responsibilities.
- Shows the consiquential result for violations.
4. What are the 5 main technology security risks
1)Human Error
2)Natural Disasters
3)Technical Failures
4)Deliberate Acts
5)Management Failure
5. Outline one way to reduce each risk
1) Human error: Strong passwords which consists of some letters and numbers make it harder to guess the password and prevent people guessing passwords.
2) Natural disaster: Retaining offsite backups which are kept outside of the premises and are kept in the exact same order as on premises.
3)Techinical Failures: Network rights and permissions correctly assigned reduce the risk of employees accessing parts of the system which could result to failures.
4)Deliberate Acts- Passwords: Changing passwords on a regular basis with a secure password reset,will decrease the prevention of external parties hacking into systems.
5) Management Failure: Training employees on the job helps employees to develop the correct skills needed to perform their tasts with minimal risks involved.
6. What is a disaster recovery plan, what strategies might a firm employee?
The process of regaining information and data after a disaster has taken place. It is a form of Off Site Backups- This involves saving information and data outside of the workplace, so there will be a copy available if something goes wrong in the workplace.
- Privacy Issues: Consists of the interest of the business for keeping valuable information away from the public. This relates to confidentiality. This is kept in mind when a company has valuable infromation which is wanted to be kept private. The risk of being released in the public could result to the company 'sinking'.
- Data Accuracy: It is important that data is keep up to date and is as accurate as possible. Constant checks must be made to ensure that no 'suspicious' activity has occured. Data must also be limited to who can access it to decrease amounts of malicious activity.
- Property Issues: Issues with who owns information in companies is a problem. It is shown that most companies are montioring employees' emails as they are misusing them with the information which is being issued out to peole outside of the company.
2. Describe a situation involving technology that is ethical but illegal
Employees search organisational database for sensitive and personal information. This is an example of bank employees who have access to customers' bank details and use it against their will to trace their bank details, which could lead to fraudulent activity such as taking money out of their accounts.
3. Describe and explain one of the computer use policies that a company might employee
Internet use policy- Consists of generalpriciples which guide the correct use of the internet in the workplace. The policy:
- Describes available internet services.
- Defines the purpose and restriction of internet access.
- Describes user responsibilities.
- Shows the consiquential result for violations.
4. What are the 5 main technology security risks
1)Human Error
2)Natural Disasters
3)Technical Failures
4)Deliberate Acts
5)Management Failure
5. Outline one way to reduce each risk
1) Human error: Strong passwords which consists of some letters and numbers make it harder to guess the password and prevent people guessing passwords.
2) Natural disaster: Retaining offsite backups which are kept outside of the premises and are kept in the exact same order as on premises.
3)Techinical Failures: Network rights and permissions correctly assigned reduce the risk of employees accessing parts of the system which could result to failures.
4)Deliberate Acts- Passwords: Changing passwords on a regular basis with a secure password reset,will decrease the prevention of external parties hacking into systems.
5) Management Failure: Training employees on the job helps employees to develop the correct skills needed to perform their tasts with minimal risks involved.
The link above describes how security online has changed in today's world.
6. What is a disaster recovery plan, what strategies might a firm employee?
The process of regaining information and data after a disaster has taken place. It is a form of Off Site Backups- This involves saving information and data outside of the workplace, so there will be a copy available if something goes wrong in the workplace.
The link above desribes ways which disaster recovery plans could be implemented
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)